Bacterial Contamination and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Al Anbar Province Water Sources
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/P312Keywords:
Bacterial Contamination, Antimicrobial Resistance, Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria, Water Quality, Al Anbar Province, Iraq, Antibiotic Stewardship, Molecular Resistance Genes.Abstract
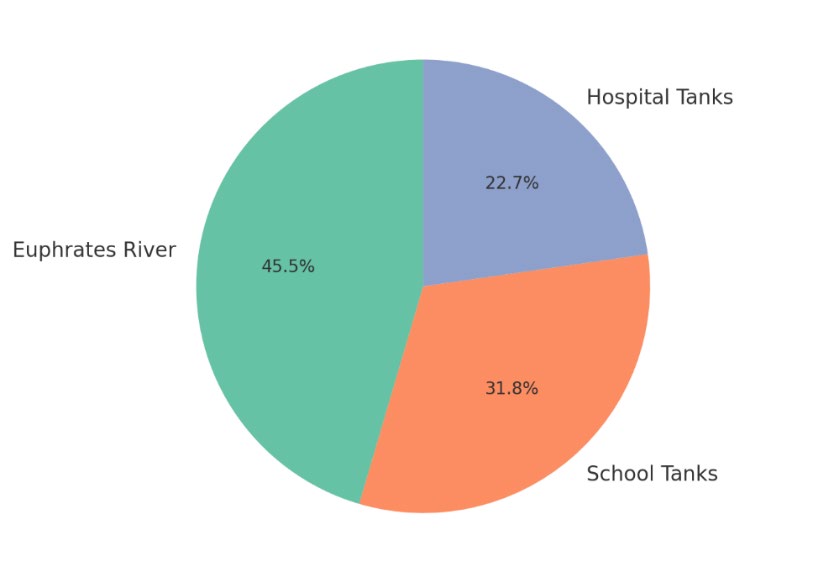
Bacterial pollution and antibiotic resistance pose substantial public health issues in Anbar Governorate, Iraq. Contamination of environmental water sources and the rise of multidrug-resistant bacterial phenotypes pose significant threats to public health and the effectiveness of healthcare systems. This study sought to assess bacterial contamination levels, delineate antibiotic resistance patterns, and analyze the genetic properties of the primary bacterial pathogens in the region. Approaches: Clinical and environmental specimens, including water samples, were collected from the Euphrates River, institutional water storage facilities, and healthcare institutions. Specimens received thorough microbiological analysis, encompassing bacterial culture, biochemical characterization, and molecular identification for accurate strain designation. Antimicrobial susceptibility was assessed using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method, with resistance profiles analyzed in accordance with Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) criteria. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was utilized to identify resistance determinants, specifically the blaCTX-M, blaNDM, and mexA/mexB genes. Statistical studies were performed to clarify resistance patterns and evaluate relationships among various sample sources, thoroughly defining regional bacterial resistance trends. Outcomes: Analysis indicated heightened bacterial contamination in the Euphrates River, with total coliform and fecal coliform levels surpassing acceptable limits. Water quality degradation was significant, as shown by large bacterial loads from institutional water sources. The most common isolates were Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with high levels of resistance against antimicrobials, including ceftriaxone (85-90%), ciprofloxacin (55-80%), and meropenem (60-95%). Molecular characterization showed that important resistance determinants were common, with blaCTX-M being the major factor identified among K. pneumoniae isolates and mexA/mexB genes indicating multidrug resistance in P. aeruginosa. Results of statistical analyses highlighted significant correlations between levels of contamination with a range of sources and patterns of antimicrobial resistance, solidifying the increasing threats from bacterial contamination and antimicrobial resistance in the region. The results revealed that water sources in Anbar Governorate are critical bacterial contamination locations, and the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance within clinical and environmental isolates reached high levels. While our findings reveal new determinants of resistance, they highlight the need for improved infection control policies, robust antimicrobial stewardship, and coordinated water treatment strategies. Reducing resistant bacterial spread requires intervention based on bringing together public health authorities, health care providers, and environmental agencies to guarantee better water quality and health benefits population.
References
Taha AMA, Shratooh SM, Jasim AH. Determination of bacterial pollution levels in Euphrates River within Al-Anbar Province, Iraq. Iraqi J Agric Res. 2023;27(1).
Najeeb LM, Shartooh SM, Yaqob HK. Detection of bacterial pollution from school drinking water tanks in the Habbaniyah district, West of Iraq. Iraqi J Sci. 2024;65(11):6392-6404.
Al-Qaysi AM, Ahmed MM, Habeeb WH, Al-Meani SAL, Al Janaby MS, Alalwani AK, et al. Genetic variants of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from Al-Ramadi Teaching Hospital, Iraq. Open Microbiol J. 2024;18:e18742858298979.
Abbas DA, Al-Janabi AO, Waleed N. Bacterial infection in male infertility in Al-Anbar Province, West of Iraq. Egypt Acad J Biol Sci. 2019;11(1):35-40.
Al-Ani RM, Al-Zubaidi MI, Lafi SA. Profile of aerobic bacteria and their antibiotic sensitivity in chronic suppurative otitis media in Al-Ramadi Teaching Hospital, Ramadi City, Iraq. Qatar Med J. 2021;2021(3).
Ali WMA, Al Fakhar SA, Mohammed SH, Mohammed KIA, Mousa JM. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance among patients in Iraqi hospitals. Haya Saudi J Life Sci. 2023;8(7):118-126.
Thamer AK. Prevalence and surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in society of Basra-Iraq. World J Pharm Sci Res. 2023;2(6):134-139.
Oudah MA. Antibiotic resistance profile of pathogenic bacteria isolated from healthcare rooms in the Mosul Government Hospital, Iraq. Med J Babylon. 2024;21(S1):S70-S80.
Salman HA, Alhameedawi AK, Alsallameh SMS, Taha GM. Prevalence of multi-antibiotic-resistant bacteria isolated from children with urinary tract infection from Baghdad, Iraq. Microbiol Biotechnol Lett. 2022;50(1):147–156.
Hameed HG. Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemiology and antibiotic resistance: A five years retrospective study in Iraq. Al-Esraa Univ Coll J Med Sci. 2023;4(6):Article 3.
Issa FA. Antibiotic resistance patterns of common uropathogens isolated from females at Zakho City, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Sci J Univ Zakho. 2024;12(4):490–496.
Fayad AA, Rizk A, El Sayed S, Kaddoura M, Jawad NK, Al-Attar A, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and the Iraq wars: Armed conflict as an underinvestigated pathway with growing significance. BMJ Glob Health. 2023;7:e010863.
M’Aiber S, Maamari K, Williams A, Albakry Z, Taher AQM, Hossain F. The challenge of antibiotic resistance in post-war Mosul, Iraq: An analysis of 20 months of microbiological samples from a tertiary orthopedic care centre. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2022;30:311–318.
Lames H. ALManseeqanaa, Mohammed Razzak Ali, & Raed H. Ogaili. The Activity of Nourseothricin. Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2024; 1(2), 18-27. https://doi.org/10.59675/M124
Nisreen Jawad Kadhim, Samir F. Hassan, & Mohammed R. Ali. The Most Common Isolated Pathogen Bacteria from Post-Surgical Operation Cases. Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2024;1(2), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.59675/M121
Lames H Almanseekanaa. Molecular Study of Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolation from Clinical Samples. Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2022; 1(1), 06-14(2022). https://doi.org/10.59675/M2022-02
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Pure Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








