Biofilm Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated from Oral Infections
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/P311Keywords:
Biofilm formation, Staph. aureus, and Oral infections.Abstract
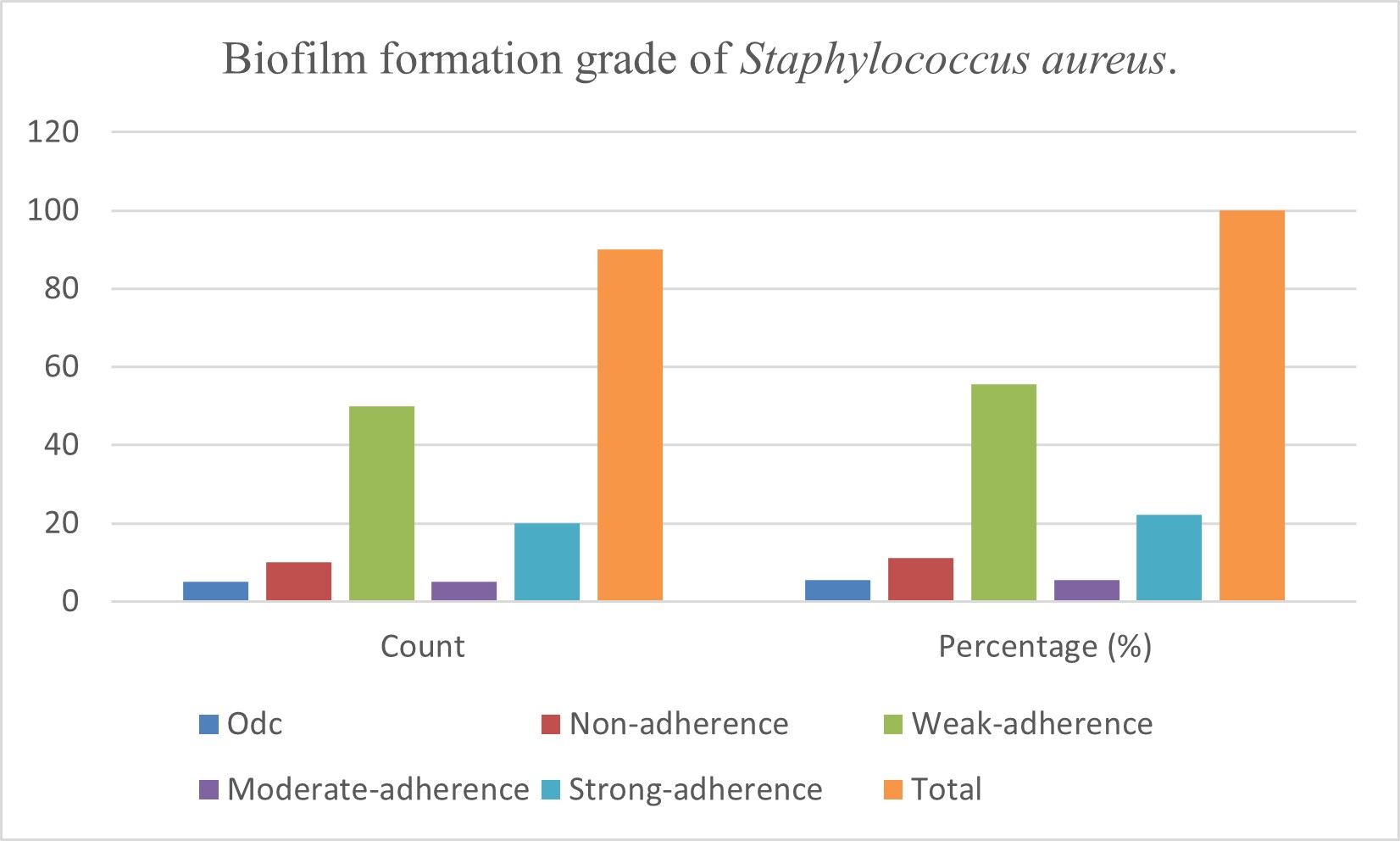
This work involves identifying biofilm development by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from oral infections. Biofilm formation transpires due to bacterial activity influenced by multiple elements that create an oral environment conducive to its development, as biofilm formation is a critical pathogenicity factor for bacteria. This investigation involved the collection of forty clinical samples from the oral cavities of individuals with oral issues. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated and identified using several methods, with confirmation via polymerase chain reaction (PCR), yielding 28 positive samples and 12 negative samples. Bacteria can establish biofilms on biological and abiotic surfaces in both natural and clinical settings. Bacterial aggregation within biofilms is created by the extracellular matrix they secrete. Staphylococcus aureus is a common pathogen linked to biofilm infection. The assessment of biofilm formation on polymeric surfaces by Staphylococcus aureus isolates was conducted utilizing the crystal violet microtiter plate technique. Crystal violet is a negative stain that exhibits affinity for positively charged molecules on the cell surface, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides. The extent of biofilm formation was quantified using optical density (OD) values, which were compared to the control OD (ODc); the classifications resulted in 21 highly adherent samples, 8 lightly adherent, 49 barely adherent and 12 nonadherent.
References
Donlan RM, Costerton JW. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(2):167–93. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.2.167-93.2002.
Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE, Korber DR, Lappin-Scott HM. Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995; 49:711–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003431.
Kristian SA, Golda T, Ferracin F, Cramton SE, Neumeister B, Peschel A, et al. The ability of biofilm formation does not influence virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and host response in a mouse tissue cage infection model. Microb Pathog. 2004;36(4):237–45. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2003.12.004.
Donlan RM, Costerton JW. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(2):167–93.
Mulvey MR, Simor AE. Antimicrobial resistance in hospitals: how concerned should we be? CMAJ. 2009;180(4):408–15. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.080239.
Kot B, Wierzchowska K, Piechota M, Grużewska A. Antimicrobial resistance patterns in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from patients hospitalized during 2015–2017 in hospitals in Poland. Med Princ Pract. 2020;29(1):61–8. doi: 10.1159/000501788.
Cheung GY, Bae JS, Otto M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence. 2021;12(1):547–69.
Kakoullis L, Papachristodoulou E, Chra P, Panos G. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in important Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens and novel antibiotic solutions. Antibiotics. 2021;10(4):415.
Guo H, Tong Y, Cheng J, Abbas Z, Li Z, Wang J, et al. Biofilm and small colony variants—an update on Staphylococcus aureus strategies toward drug resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1241. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031241.
James C, Natalie S. Microbiology: A laboratory manual. Pearson Education; 2014. Available from: https://lib.hpu.edu.vn/handle/123456789/28998.
Javid F, Taku A, Bhat MA, Badroo GA, Mudasir M, Sofi TA. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus based on coagulase gene. Vet World. 2018;11(4):423–30. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.423-430.
Stepanović S, Vuković D, Dakić I, Savić B, Švabić-Vlahović M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods. 2000;40(2):175–9.
Zhou Y, Millhouse E, Shaw T, Lappin DF, Rajendran R, Bagg J, et al. Evaluating Streptococcus mutans strain-dependent characteristics in a polymicrobial biofilm community. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1498.
Stepanović S, Vuković D, Dakić I, Savić B, Švabić-Vlahović M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods. 2000;40(2):175–9.
Abbasi Montazeri E, Khosravi AD, Khazaei S, Sabbagh A. Prevalence of methicillin resistance and superantigenic toxins in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from patients with cancer. BMC Microbiol. 2021;21(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02319-7.
Ghayyib Arif A, Ahmed Ibrahim A, Ahmed Hamid K. Isolation, molecular identification, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. HIV Nurs. 2022;22(2):278–83.
Ghaderi H, Malekabad E, Vahidi M, Dadashi A. Evaluation of genotypic and phenotypic biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples and their association with antimicrobial resistance. Iran J Med Microbiol. 2020;14(5):441–59.
Zhou X, Li Y. Atlas of oral microbiology: From healthy microflora to disease. Springer Nature; 2021.
Djordjevic D, Wiedmann M, McLandsborough L. Microtiter plate assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68(6):2950–8.
Grivet M, Morrier J, Benay G, Barsotti O. Effect of hydrophobicity on in vitro streptococcal adhesion to dental alloys. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2000;11(10):637–42.
Stewart PS. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002;292(2):107–13. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00196.
Romero D, Aguilar C, Losick R, Kolter R. Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(5):2230–4.
Huh AJ, Kwon YJ. “Nanoantibiotics”: a new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics-resistant era. J Control Release. 2011;156(2):128–45.
Herman-Bausier P, El-Kirat-Chatel S, Foster TJ, Geoghegan JA, Dufrêne YF. Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin-binding protein A mediates cell-cell adhesion through low-affinity homophilic bonds. mBio. 2015;6:e00413-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00413-15.
Rasamiravaka T, Labtani Q, Duez P, El Jaziri M. The formation of biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a review of the natural and synthetic compounds interfering with control mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:759348. doi: 10.1155/2015/759348.
Rawaa Thamir Alasadi, Rasha Mohammed Hayder, Hassanain Jwad Abidalhussein. The Potential of Urease Enzyme from Staphylococcus Aureus to Stabilize Blood Concentration Levels. Aca. Intl. J. M. U 2024 2(2):1-6: DOI: https://doi.org/10.59675/U221
Nisreen Jawad Kadhim, Samir F. Hassan, Mohammed R. Ali. The Most Common Isolated Pathogen Bacteria from Post-Surgical Operation Cases. Aca. Intl. J. Med. Sci. 2024;1(2):1-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59675/M121
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Pure Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








