Comparative Histological Changes to Investigate the Therapeutic Effect of Cefaclit+ Cream and Penicillin-Streptomycin on Wound Healing In Rabbits
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/P316Keywords:
Wound healing, Postbiotic Cicalfate+ cream, penicillin-streptomycin, rabbits.Abstract
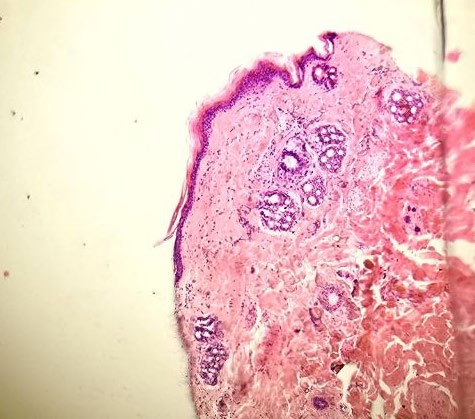
The present study was designed to evaluate the comparative effect of cefaclor+ cream and penicillin-streptomycin on the histology of rabbits' healing processes in full-thickness skin wounds. All rabbits were forty-five healthy adult bucks weighing between 1.3 and 1.8 kg were made A full-thickness wound measuring 2.5 x 2.5 cm was made in the dorsal back area. Intramuscular injections of xylazine hydrochloride (5 mg/kg), ketamine hydrochloride (35 mg/kg) were given very quickly (IM), along with 1 mg/kg of diazepam. These animals were separated into three groups (A, B and C groups) The first group was treated intramuscular with penicillin-streptomycin daily with single dose (group A), and the second group was given cicalfate+ cream topically twice daily (group B), the last group designated as (group C) served as the control and didn't receive any treatment. For histopathological evaluation, on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days after wounding, the fifteen male adult rabbits that were chosen for the morphological investigation were separated into three subgroups of five. Histological analysis demonstrated that wound healing was more organized and efficient in group (B) compared to the other groups, with group (A) showing a moderate degree of improvement, and the rate of healing highly in group (B) than other groups which led to highly attachment between layers of skin resulting in good blood supply and nutrition also greater cellularity and finally faster healing to the wound.
References
Eroschenko VP. DiFiore's Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations. 11th ed. South Asian Edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013. p. 216–24.
Daeschlein G. Antimicrobial and antiseptic strategies in wound management. Int Wound J. 2013;10(Suppl 1):9–14.
Weledji EP. Perspectives on wound healing. Austin J Surg. 2017;4(3):1104.
Sen CK. Human wound and its burden: Updated 2020 compendium of estimates. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021;10:281–92.
Martin P, Nunan R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:370–8.
Dreifke MB, Jayasuriya AA, Jayasuriya AC. Current wound healing procedures and potential care. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;48:651–62.
Sorg H, Tilkorn DJ, Hager S, Hauser JR, Mirastschijski U. Skin wound healing: an update on the current knowledge and concepts. Eur Surg Res. 2017;58:81.
Bõsze Zs, Houdebine M. Application of rabbits in biomedical research: a review. World Rabbit Sci. 2006;14:1 14.
Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:265sr6.
Zimmermann A, Truss F. The effect of antibiotic drugs on wound-healing. Urol Res. 1974;2:73 7.
Wang P, Wang S, Wang D, Li Y, Yip RCS, Chen H. Postbiotics—peptidoglycan, lipoteichoic acid, exopolysaccharides, surface layer protein and pili proteins: Structure, activity in wounds and their delivery systems. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;274(Pt 1):133195.
Rawal S, Ali SA. Probiotics and postbiotics play a role in maintaining dermal health. J R Soc Chem. 2023. [Special Issue; online].
Lukic J, Chen V, Strahinic I, Begovic J, Lev-Tov H, Davis SC, et al. Probiotics or pro-healers: the role of beneficial bacteria in tissue repair. Wound Repair Regen. 2017;25(6):912–22.
Salaran M, Oryan A, Nikahval B, Kamali A, Ghaemi M, Abbasi-Teshnizi F, et al. Topical application of Lactobacillus plantarum on burn wound healing in diabetic rats. Iran J Vet Surg. 2019;14(1):60–72.
Jamaran S, Jafari P, Marjani A, Akbari N, Feizabad MM. Novel wound dressing based on postbiotic/chitosan film accelerates cutaneous wound healing. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2021;14(12):e120806.
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Garcia-Varela R, Garcia HS, Mata-Haro V, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Cordoba B, et al. Postbiotics: an evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2018;75:105–14.
García-Vicente EJ, Rey-Casero I, Martín M, Pérez A, Benito-Murcia M, Risco D. Oral supplementation with postbiotics modulates the immune response produced by myxomatosis vaccination in wild rabbits. Vaccine. 2024;42:125978.
Avene. Cicafate Sell Sheet Cream Scar Gel Hand Lips. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.avene.com/media/marketing/assets/Cicalfate_Sell_Sheet_Cream_Scar_Gel_Hand_Lips.pdf
Albozachri JMK, Hameed FM, Al-Tomah HM, Muhammid HA. Evaluation of two general anesthetic regimens using xylazine and ketamine with atropine and diazepam in rabbits. J Univ Kerbala. 2017;15:21 30.
Pujadas R, Escriva E, Jane J, Fernandez F, Fava P, Garau J. Comparative capacity of orally administered amoxicillin and parenterally administered penicillin-streptomycin to protect rabbits against experimentally induced streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986;29(5):909–12.
Luna LG. Histopathologic methods and color atlas of special stains and tissue artifacts. Maryland: American Histolabs Inc.; 1992.
Proksch E, Brandner JM, Jensen JM. The skin: an indispensable barrier. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17(12):1063–72.
Lin PH, Sermersheim M, Li H, Lee PHU, Steinberg SM, Ma J. Zinc in wound healing modulation. Nutrients. 2018;10(1):16.
Henzel JH, DeWeese MS, Lichti EL. Zinc concentrations within healing wounds. Significance of postoperative zincuria on availability and requirements during tissue repair. Arch Surg. 1970;100:349–57.
Lansdown IBG, Mirastschijski U, Stubbs N, Scanlon E, Agren MS. Zinc in wound healing: theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15:2–16.
Rajab AM, Al-Wattar WT, Taqa GA. The roles of apigenin cream on wound healing in rabbit models. J Appl Vet Sci. 2022;7(1):1–5.
Ersoz M, Koc A, Acar Ulutas P, Serefoglu F. [Title missing]. J Biol Life Sci. 2017;8(2). [Please provide the full article title for complete citation.]
García-Vicente EJ, Rey-Casero I, Martín M, Pérez A, Benito-Murcia M, Risco D. Oral supplementation with postbiotics modulates the immune response produced by myxomatosis vaccination in wild rabbits. Vaccine. 2024;42:125978.
Abd Alrahma HM, Abdulraza AW, Kareem DA. Study of the histological structures of skin affected with N-acetylcysteine in rabbits. Turk J Physiother Rehabil. 2021;32(3).
Bainbridge P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J Wound Care. 2013;22(8):407–8.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Pure Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





